- 정의
데이터를 링크로 연결해서 관리하는 자료구조
자료의 순서는 정해져 있지만, 메모리상 연속성이 보장되지는 않음
- 장점
데이터 공간을 미리 할당할 필요가 없음 -> 리스트의 길이가 가변적이라 데이터 추가/삭제 용이
- 단점
연결구조를 위한 별도 데이터 공간 필요
연결 정보를 찾는 시간이 필요(접근속도가 상대적으로 느림)
데이터 추가, 삭제 시 앞뒤 데이터의 연결을 재구성하는 작업 필요
- 기본 구조
노드 : 데이터 저장 단위로 , 값과 포인터로 구성
포인터 : 다음 노드나 이전 노드의 연결 정보
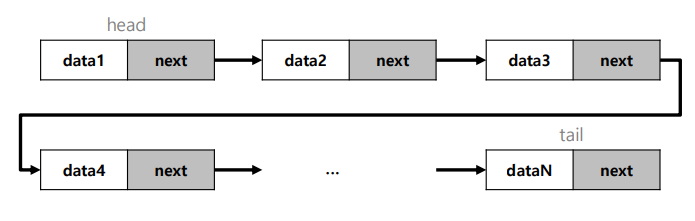
노드 하나에 값이나 포인터가 여러 개가 있을 수 있다.
- 데이터 추가
데이터 추가위치(head, 중간, tail)에 따른 연결 작업이 필요하다
예시) 데이터를 가장 앞에 추가할 때
- 추가할 데이터를 담을 노드 생성
- 링크 연결 작업
- head 이전 작업
예시) 데이터를 맨 뒤에 추가할 때
- 추가할 데이터를 담을 노드 생성
- head부터 끝 노드까지 순회
- 링크 연결 작업
예시) 데이터를 중간에 추가할 때
- 추가할 데이터를 담을 노드 생성
- head부터 데이터 추가 위치 직전 노드까지 순회
- 링크 연결 작업
- 데이터 삭제
예시) 맨 앞의 데이터를 삭제
- 삭제 대상 노드 지정 (delete_node)
- head 이전 작업
- delete_node 삭제
예시) 맨 뒤의 데이터를 삭제
- head로부터 가장 끝까지 순회
- 끝노드 삭제
- 삭제 이전 노드의 링크 처리
// 단방향 연결리스트 구현
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
class LinkedList {
Node head;
public LinkedList() {
}
public LinkedList(Node head) {
this.head = head;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.head == null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void add(int data) {
Node node = new Node(data, null);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
return;
} else {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}
public void remove() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
Node prev = cur;
while (cur.next != null) {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = null;
} else {
prev.next = null;
}
}
public void find(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
System.out.println("Data exist!");
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("Data not found!");
}
public void showAll() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList myList = new LinkedList(new Node(1, null));
myList.showAll();
myList.add(2);
myList.add(3);
myList.add(4);
myList.add(5);
myList.add(6);
myList.showAll();
myList.remove();
myList.remove();
myList.remove();
myList.remove();
myList.remove();
myList.showAll();
myList.remove();
myList.remove();
myList.remove();
}
}'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 해시 테이블 (Hash Table) (0) | 2022.04.06 |
|---|---|
| 데크 (Deque) (0) | 2022.04.06 |

댓글